Key Takeaways
- Civil works form the foundation of modern infrastructure.
- They include earthworks, road systems, drainage, utilities, and structural foundations.
- The civil works process follows clear steps from planning to inspection, testing, and turnover.
- Engineers, project managers, contractors, and skilled workers collaborate to deliver safe and effective civil works.
- Civil works support national development and long-term sustainability.
Civil works shape the foundation of every modern community. They support the movement of people, the flow of resources, and the structures that define a city’s growth.
But what exactly are civil works in construction and why are they vital to any project, big or small?
This guide explains what civil works include, how the process unfolds, and who performs each phase.
You will also understand why civil works matter in building a future-ready Philippines.
What Is Civil Works in Construction
Civil works refer to the construction and improvement of essential infrastructure. These involve earthworks, roads, bridges, drainage, water systems, structural foundations, and other works that prepare and support the built environment.
Civil works focus on transforming land into stable, functional, and safe environments. While building construction deals with structures like homes or offices, civil works ensure that the land can support those structures and that communities have the systems they need to thrive.
Civil works power mobility, safety, and long-term progress. They are the groundwork of nation-building and development.
The Full Scope of Civil Works
Civil works cover a wide range of activities. Some are visible, such as roads and bridges, while others operate underground through pipelines and drainage networks.
Earthworks and Site Preparation
This is where construction begins. Earthworks include:
- Excavation and backfilling
- Grading and leveling
- Soil compaction
- Slope protection and erosion control
These tasks stabilize the land, control water flow, and make the site safe for future construction.
Road and Transportation Systems
Civil works support safe and efficient movement. They cover:
- Highways and roads
- Bridges and flyovers
- Tunnels
- Access roads and walkways
Strong transport systems boost economic activity and improve daily life.
Water and Utility Systems
Communities depend on reliable water and sanitation. Civil works include:
- Drainage systems
- Sewage and wastewater lines
- Stormwater systems
- Water pipeline installations
- Flood control mechanisms
These systems improve safety, sanitation, and environmental protection.
Structural Components and Foundations
Foundations must withstand heavy loads and natural challenges. Civil works build:
- Foundation systems
- Retaining walls
- Footings and concrete structures
These elements keep buildings and infrastructure durable and safe.
Public and Industrial Infrastructure
Civil works extend to major developments such as:
- Airports and seaports
- Public terminals
- Pumping stations
- Industrial site developments
These projects support national growth and strengthen the country’s infrastructure network.
Environmental and Sustainable Works
Modern construction prioritizes sustainability. Civil works may include:
- Slope protection
- Drainage that reduces flooding
- Greener land development practices
These solutions help manage resources responsibly and support long-term resilience.
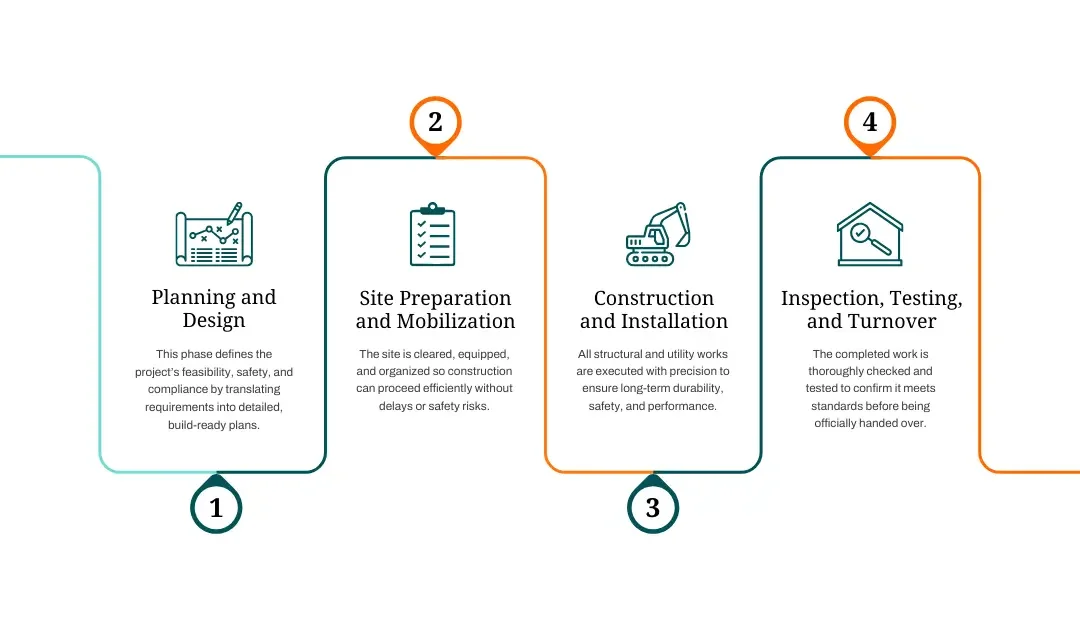
The Civil Works Process
Civil works follow a structured process to ensure quality, safety, and efficiency.
1. Planning and Design
This phase includes surveys, engineering designs, feasibility studies, and safety assessments.
Each detail is analyzed so the project meets regulatory standards and client expectations. Proper planning sets the foundation for success.
2. Site Preparation and Mobilization
Before construction begins, the site is prepared. Tasks include:
- Clearing debris
- Setting up temporary facilities
- Mobilizing equipment and materials
- Preparing access points and utilities
This step ensures smooth operations throughout the project.
3. Construction and Installation
The core phase includes:
- Excavation and land shaping
- Installing drainage and pipelines
- Pouring concrete for foundations
- Building bridges, retaining walls, and road systems
Precision and accountability are essential, as this phase defines the long-term safety and quality of the project.
4. Inspection, Testing, and Turnover
Engineers and inspectors check all components to ensure compliance with standards. Testing confirms that systems work properly before the project is turned over.
Who Performs Civil Works
Civil works require a collaborative effort among experts and skilled teams.
- Civil Engineers: They design structural systems, analyze soil conditions, and create plans for safe and stable infrastructure.
- Structural and Geotechnical Engineers: They focus on load-bearing structures, foundations, and soil behavior.
- Project Managers and Site Supervisors: They oversee project execution, timelines, communication, and safety.
- Contractors and Skilled Workers: They carry out civil works on the ground. This includes heavy equipment operators, masons, carpenters, welders, and laborers.
- Quality and Safety Teams: They ensure that all work meets safety and structural standards.
Every successful civil works project depends on coordination, discipline, and strong leadership.
Why Civil Works Matter for the Philippines
Civil works uplift communities and create safer, more connected, and more resilient spaces. They support national development by:
- Improving travel and logistics
- Strengthening public safety through better drainage and water systems
- Supporting commercial and industrial growth
- Enhancing the quality of life for communities
- Establishing foundations for world-class infrastructure
These works directly contribute to building a future-ready nation where progress is accessible to all.
Building Strong Foundations for a Future-Ready Nation
Civil works are vital to creating safe, functional, and future-ready spaces. They prepare the land, support major systems, and build the infrastructure that keeps communities moving and growing. As the Philippines continues to advance, civil works will shape the landscapes that define our progress.
If your project requires reliable, modern, and high-quality civil works, partner with ABI. Our team is committed to delivering future-ready solutions that bring your vision to life with excellence, integrity, and precision.
FAQs
What does civil works mean in construction?
Civil works include the construction and improvement of basic infrastructure such as roads, drainage, water systems, and structural foundations. These are the works that prepare and support the entire project site.
What is included in civil works?
Civil works cover earthworks, road construction, bridges, drainage systems, pipelines, foundations, and public infrastructure. These tasks shape the land and make it safe and ready for development.
How is civil works different from building construction?
Civil works focus on land development and infrastructure, while building construction focuses on homes, offices, or commercial spaces. Civil works make sure the site is stable, safe, and ready before any structure is built.
Who performs civil works?
Civil works are done by civil engineers, project managers, contractors, skilled workers, and heavy equipment teams. Each group has a vital role in planning, building, and completing the project.
Why are civil works important?
Civil works support transportation, drainage, utilities, and public safety. They create strong foundations for buildings and communities, helping cities grow and function well.